1. Overview
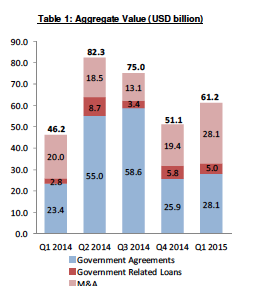
Q1 Chinese outbound investments totalled USD 61.2 billion, an increase of 19.8% over Q4 2014. There was a substantial pick up in M&A in aggregate value (up 45% from Q4) and a 5 quarter high, but a slight decrease in volume (down 11% from Q4). Government Related Loan Agreements, outside of the more comprehensive Government Agreements signed this quarter were USD 5.0 billion, continuing the downward trend over the past few quarters. The aggregate value of Government Agreements rose 8.5% from Q4 2014 to USD 28.1 billion, led by major agreements with Argentina, Kazakhstan and Ecuador.
M&A / Equity Transactions
China outbound M&A / equity aggregate value was USD 28.1 billion, up 45% versus Q4, and up 43% versus the average of the past five quarters. The strong jump in M&A equity aggregate value in Q1 was heavily influenced by large transactions. There were 8 acquisitions of controlling stakes greater that USD 1 billion, including the ChemChina / Pirelli deal, which involved USD 7.7 billion in equity plus the assumption of USD 1.2 billion of long term debt. In addition, there were 5 other M&A transactions greater than USD 450 million in value. There was also a $500 million minority investment in an Indian technology company. Collectively, these 14 transactions accounted for over 80% of aggregate value during Q1.
Transactions in the Technology sector led in volume with total 28 transactions. The Financial sector (which includes real estate) ranked second with 27 transactions. The Consumer Goods and Services sector ranked third with 17 transactions, followed by Industrials, Oil & Gas and Healthcare each with 5 transactions / investments.
The Consumer Goods and Services sector led with aggregate value of USD 10.7 billion due mostly to the Pirelli deal, while Financials, driven by a series of commercial real estate M&A transactions, followed with USD 9.7 billion.
North America led with 33 transactions (as discussed below, many of these were ecommerce / technology investments) followed by Asia with 31 then Europe with 25. Collectively, these three continents represented 95% of all M&A / equity aggregate value and 88% of total volume.
Overall transaction size was slightly below USD 280 million; however, this average varies considerably among industries. For example, in Financials, the average transaction size was USD 360 million, while among Technology investments, the average size was slightly under USD 100 million.
Change in Equity Component / Content Inclusions
For the past several quarters, China has been investing aggressively in internet / ecommerce businesses both inside and outside of China. Historically, we have omitted such equity investments from this document, and instead included them in a separate database. In light of the recently increased volumes and aggregate amounts by major Chinese organisations such as Alibaba, Tencent, Baidu, RenRen, Fosun and many others, we have now included all such equity investments into this database.
The table below demonstrates the increased investment appetite for small such investments in overall volumes, and 2014 restated aggregate volumes by quarter.
Table 2: Equity Investments including E-Commerce / Technology
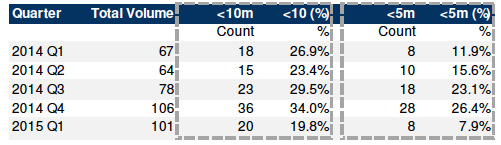
Table 1 at the top of Page 1, also now includes all restated aggregate values in 2014 for such equity investments.
Government Related Loan Agreements
This quarter there were 9 Government Related Loan Agreements outside of larger Government Agreements, totalling USD 5.0 billion. This amount represents a 36% decrease in volume and a 14% decrease from Q4 2014 revised total loan amounts. There were 5 loans each over USD 500 million as set out on pages 16-17 (for subscription clients). Four of these 5 loans involved Ecuador (USD 7.5 billion) and Indonesia (USD 2.7 billion). All 13 of these loans were to emerging markets based borrowers. CEXIM was involved in 11 of these while CDB was involved in the other 2.
Please note that we did not yet include the USD 10 billion credit facilities being discussed between China and Venezuela this quarter as it has not been agreed or approved.
Government Agreements
In Q1, there were 6 Government Agreements signed, 3 with specific values disclosed, which totalled USD 28.1 billion. Aggregate values increased by 8.5% from Q4 2014.
Four of these larger Agreements were signed as part of visits to China by senior leaders of the visiting government, while one involved Sri Lankan President Sirisena visiting President Xi in Beijing.
II. Quarterly Feature: Silk Road Fund Becomes Operational
In November 2014, President Xi announced the creation of the Silk Road Fund (“SRF”), which was established in late December and then proclaimed as "active" in February. The planned USD 40 billion fund was initially funded through USD 10 billion of contributions from four major domestic Chinese organisations: USD 6.5 billion from SAFE, USD 1.5 billion each from CIC and CEXIM and USD 500 million from CDB.
We believe that China views the SRF to be similar to the World Bank's investment arm (IFC) and African Development Bank's Mutual Development Fund. In this regard, the SRF is designed to take emerging market equity risk in infrastructure and resource development projects for which it anticipates "reasonable returns". The SRF is also able to draw upon the prior equity investment experience of SAFE and CIC as well as the bank financing experience of CDB and CEXIM.
While China expects to invest as much as USD 800 million in the New Silk Road and Maritime Silk Route, this fund is not, in the words of its Head, Jin Qi, "an aid agency".
As all of the USD 10 billion has been contributed from domestic Chinese institutions and since none of the funding has left the country, we have not included the USD 10 billion in our quarterly totals, although, again, the SRF is now active.